
One had to provide a VCS root branch specification like refs/pull/*/head for that. It is possible to configure TeamCity to run builds on GitHub pull request branches. In fact, it proved to be so convenient that some companies started to use it even for their regular development workflows. These days pull requests is a common technique of accepting changes from third-party contributors. Take the advantage of the TeamCity-GitHub improved integration and let these features make your experience of Continuous Integration & Delivery with GitHub and TeamCity nice and smooth.Anton Arhipov The hassle with Pull Requests As an additional benefit, webhooks reduce the load on both the TeamCity server and the GitHub server. Installed GitHub webhooks greatly decrease the time required for TeamCity to detect a change.
TEAMCITY GITHUB INSTALL
Its task is to install webhooks for GitHub repositories specified in TeamCity VCS roots.


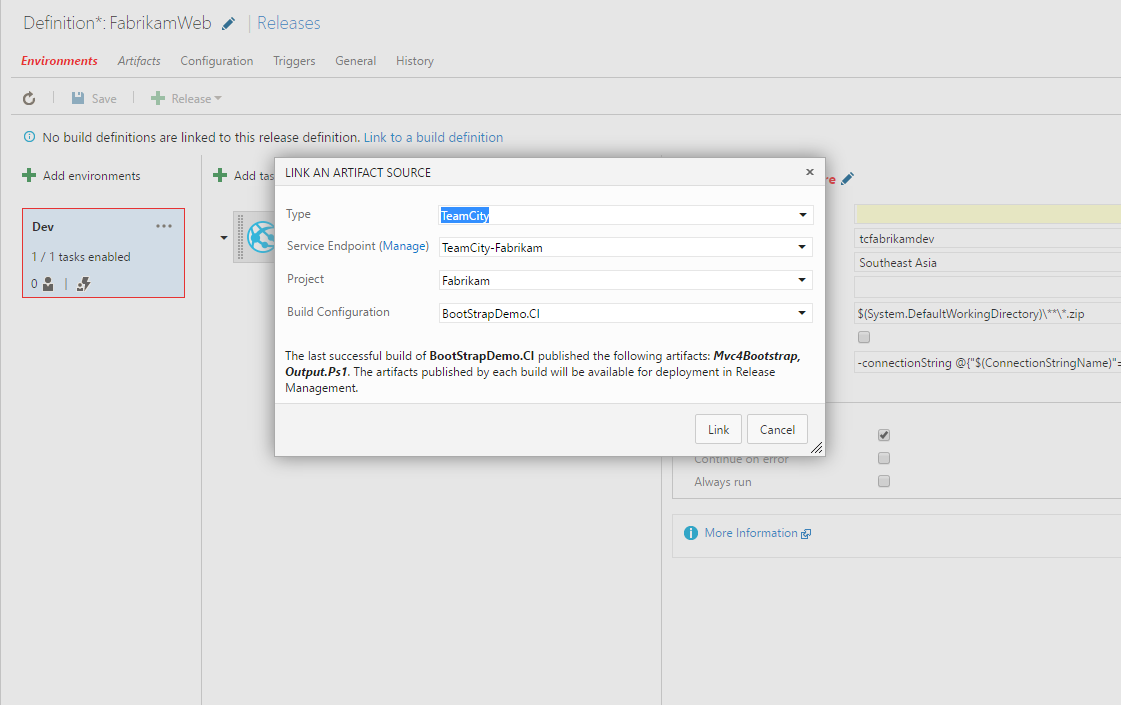
Earlier there were several external plugins allowing you to publish the TeamCity build status on GitHub, and in TeamCity 10 we delivered a bundled build feature, Commit Status Publisher, which automatically attaches the build status to your GitHub pull requests:īesides, using the TeamCity REST API, you can publish the status icon of your TeamCity build in the README for your repository:Īll the above-mentioned improvements are bundled with TeamCity 10, but we should also mention the TeamCity Commit Hooks Plugin, not bundled with TeamCity yet. This plugin is compatible with TeamCity 10 or later. TeamCity Build Status in GitHubĭevelopers find it handy to view the status of their commits right in the repository. on the Changes page, Issues tab of the build results page). #(\d+). TeamCity will resolve the issue number mentioned in a VCS comment and will display a link to this issue in the Web UI (e.g. The rest is easy – select the type of authentication and provide the required information, tell TeamCity which strings should be recognized as references to issues: for GitHub, the regex syntax is used, e.g. If no connection is configured, the URL can be specified manually. If a project level connection to GitHub is configured, you can simply select the repository URL from the list available on clicking the GitHub icon: It is configured on the dedicated page of the project settings. GitHub Issue Tracker Integration in TeamCityīuilt-in integration with GitHub issue tracker was also introduced in TeamCity 10. It makes setting up a subproject, a Git VCS root, or a GitHub issue tracker extremely easy. On clicking the icon, TeamCity will list GitHub repositories available to the user.Ĭonfiguring a GitHub connection is useful for the organization administrator who can create a parent project and configure a connection to GitHub there once thus, all the TeamCity users of the organization will see a list of GitHub repositories URLs in the TeamCity Web UI.
Once the connection is set up, you can create a project or a build configuration pointing to a GitHub repository:īesides, with the connection configured, a small GitHub icon becomes active in several places where a repository URL can be specified: create project from URL, create Git VCS root, GitHub issue tracker, create create VCS root from URL: We’ve been gradually improving the integration, and in TeamCity 10 you can now set up a connection to GitHub on the project level:

Project-level GitHub Connection in TeamCity
TEAMCITY GITHUB CODE
GitHub Issue Tracker Integration in TeamCityĬonfiguring TeamCity to use GitHub as the source code repository has always been easy, especially since the feature ‘ create from URL‘ was first introduced. TeamCity 10 has brought a number of improvements related to integration with GitHub, which are worth a special mention.Project-level GitHub Connection in TeamCity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
